Search This Supplers Products:fabric inspection machinefabric rolling machinefabric folding machinefabric cutting machinewarp beam trolleybeam stacker
- Home
- About us
- Products
- Faqs
- Fabric Inspection Machine
- Fabric Folding Machine
- Fabric Cutting Machine
- Beam Stacker
- Digital Counter Meter
- Fabric Relaxing Machine
- Tubular Fabric Reversing Machine
- Tubular Fabric Slitting Machine
- Automatic Tube-Sewing Machine
- Hydraulic Warp Beam Trolley
- Motorized Warp Beam Trolley
- Cloth Roll Trolley
- Warp Beam
- SUNTECH Service
- Fabric Rolling Machine
- Fabric Roll Packing Machine
- Accessories
- Batcher Machine
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
How good is Xinjiang cotton? Cotton non-woven fabric is better, suntech non-woven fabric organization loves human health
time2021/04/06

- The H&M Xinjiang cotton incident caused a global sensation, and the Chinese People’s Network boycotted BCI.Xinjiang cotton is good.Cotton non-woven fabric is better, suntech non-woven fabric organization loves human health
HM event
Recently, HM's slander of cotton in Xinjiang, China caused a global sensation. Brands such as Nike, IKEA, Zara, Decathlon, Uniqlo, NB, and ASICs also participated. They belong to the BCI organization like HM. The members of this organization have been criticized by the Chinese market. After the ban, the Chinese people united and refused to buy goods of these brands.
The full name of BCI is The Better Cotton Initiative, which is the Swiss Better Cotton Development Association (BCI). It was registered in 2009 and headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. It was originally intended to monitor the impact of cotton production on the environment and labor.

The cause of the HM incident stemmed from a BCI statement, which stated: “Any form of forced labor is unacceptable. If this is discovered, it will be deemed to have violated the BCI standards and the permit will be cancelled or deprived immediately.."(Click to share to LinkedIn)
BCI believes that, based on "the continuing allegations of forced labor and other human rights violations in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China" and "the increased risk of forced labor at the farm level has resulted in an unsustainable business environment", BCI made a decision, "Immediately stop all field activities in the area."
The statement did not respect objective facts and made groundless depictions of China's Xinjiang cotton. It is understood that Xinjiang cotton has gradually changed from the original manual cotton picking to the current mechanized cotton picking. In 2020, Xinjiang’s mechanical cotton harvesting area has accounted for 69.8% of Xinjiang’s total cotton farming area. The mechanical harvesting rate in northern Xinjiang has exceeded 95%, and Xinjiang’s mechanical cotton harvesting rate is expected to reach about 58%.

As the world's largest cotton consumer and the second largest cotton producer, China will produce about 5.95 million tons of cotton in 2020/2021, with a total demand of about 7.8 million tons and an annual gap of about 1.85 million tons. Among them, the output of Xinjiang cotton is 5.2 million tons, accounting for about 87% of domestic production and about 67% of domestic consumption.
China quickly countered BCI's slander. On March 24, Xinhua Net commented: H&M's behavior is really absurd! Topics such as "H&M boycott Xinjiang products" and "H&M touch porcelain Xinjiang cotton" continued to ferment on Weibo. Netizens said, "I hope these companies that distort facts and want to make Chinese money will do their own thing." . Since then, Taobao, JD, Pinduoduo and other e-commerce platforms have removed H&M related products. The H&M Mall App was removed from the mobile app stores of Xiaomi, Huawei, vivo, and Tencent. Artists Huang Xuan and Song Qian who have had business cooperation with H&M successively issued statements stating that they no longer have a cooperative relationship with H&M.
On March 25, at a regular press conference held by the Ministry of Commerce, Gao Feng, the spokesperson, responded to reporters' questions about H&M and other foreign apparel brands due to the Xinjiang cotton issue. Gao Feng said that the so-called "forced labor" in China's Xinjiang region is completely false. The pure and flawless Xinjiang cotton cannot be tarnished and discredited by any forces. We oppose any external forces' interference in Xinjiang affairs and China's internal affairs, and oppose sanctions against relevant Chinese entities and individuals based on lies and false information on the grounds of so-called Xinjiang human rights issues.(Click to share to Facebook)

Is Xinjiang cotton good?
Xinjiang cotton has attracted international attention and has become an international Internet celebrity product. Is Xinjiang Cotton Good?
Because of the harsh planting conditions of long-staple cotton and long growth period, it requires higher heat and light conditions than ordinary cotton. It is difficult to produce long-staple cotton in general areas. However, Xinjiang is arid with little rain, long sunshine hours, long frost-free period, and large temperature difference between day and night, which is very suitable for the growth of crops, especially cotton. The total output of Xinjiang long-staple cotton production has accounted for more than 30% of the world.
Xinjiang high-quality long-staple cotton, the fiber is soft and long, generally 33 ~ 39 mm, the longest can reach 64 mm; the fineness is 7000 ~ 8500 m/g, the width is 15 ~ 16 microns; the strength is high, 4 ~ 5 grams force /Root, the fracture length is 33-40 kilometers; the number of turns is 80-120/cm. Xinjiang long-staple cotton is far superior to ordinary cotton in terms of softness, gloss, skin-friendliness, breathability, and elasticity.

Xinjiang cotton's breaking strength, elongation, uniformity, maturity and other properties are very good, making it easier to be spun into yarn, and the quality of the spun yarn is also high.
Long-staple cotton is suitable for spinning high-count yarns (yarn counts above 60s), that is, very fine yarns. The higher the yarn count, the woven fabric is relatively delicate, silky, and visually high-end. It is mostly used for high value-added textiles and clothing such as high-end yarn-dyed and home textiles. The shirt of high-count cotton fabric is comfortable to wear, soft and absorbs sweat.
The long-staple cotton bedding is very comfortable in terms of comfort:
1. Strong warmth retention: the fiber is soft and long, and it can hold more air
2. Good flexibility: fineness and length are higher than ordinary cotton
3. Good drape: with silky luster
4. Good wrinkle resistance: wear-resistant and durable, not easy to pilling
5. Good moisture removal: hollow fiber, moisture absorption and ventilation
Xinjiang cotton is rich in fibers. In addition to making clothes and daily necessities, it can also make non-woven fabrics for a wide range of applications, and non-woven fabrics made of cotton are more environmentally friendly and breathable. People’s lives are inseparable from non-woven fabrics. During the epidemic, non-woven fabrics are used in the production of masks and disposable medical supplies. On weekdays, non-woven fabrics can be used to make baby diapers, wet wipes and other hygiene products. Non-woven fabrics are the same as cotton. Always care for human health. Suntech intelligent non-woven fabric machine can produce both ordinary non-woven fabric and cotton non-woven fabric, the quality is as good as Xinjiang cotton.

Nonwovens in daily life - Versatile products for modern life
Nonwovens are in almost every aspect of daily life and society. To give an idea of the variety, the sections below explain where nonwovens can be found; what the different uses are, what the advantages are, and the technologies used to manufacture them. It is widely used in these fields:Absorbent Hygiene Products,Agriculture & Horticulture,Agriculture & Horticulture,Clothing & Footwear,Construction & Building,Electrics & Electronics,Filtration,Food &Beverage,Geotextiles & Civil Engineering,Household,medical,Packaging,Protective Clothing,wipes.(try Suntech Meltblown machine)

How are nonwovens made?
baby diaper machine price in pakistan
The production of nonwovens takes place in three stages, although modern technology allows an overlapping of some stages, and in some cases all three stages can take place at the same time.
1.Web formation
Nonwovens manufacturing starts by the arrangement of fibres in a sheet or web. The fibres can be staple fibres or filaments extruded from molten polymer granules.
Illustrations of some of the methods used to form a web:
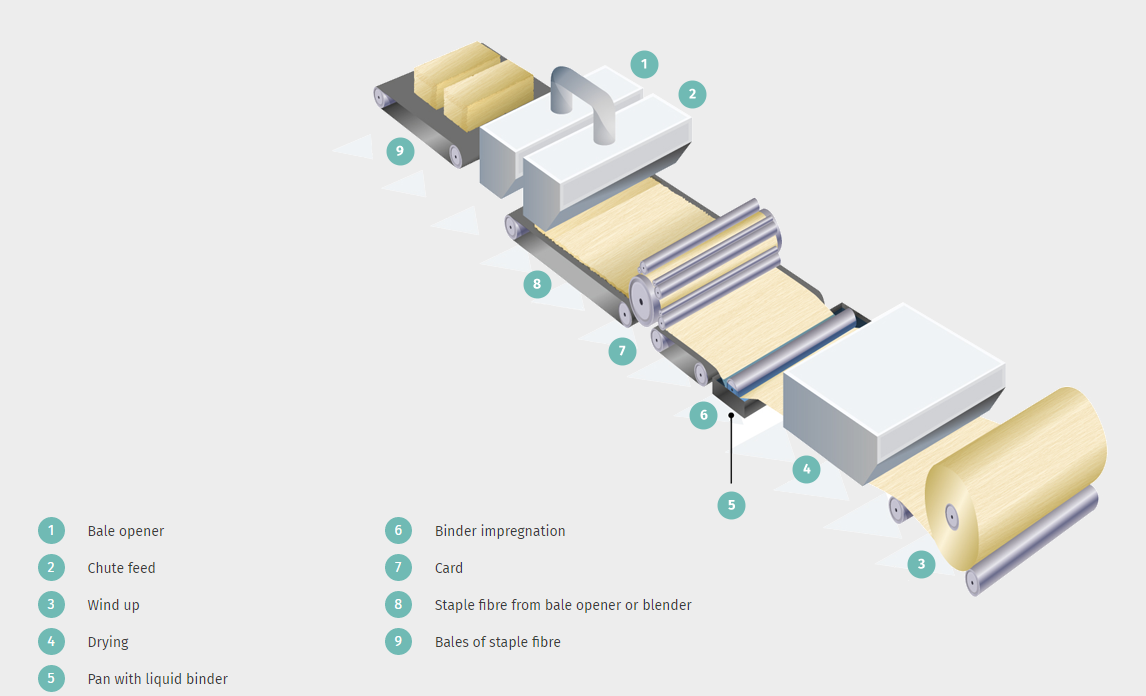
Carding is a mechanical process which starts from bales of fibres. These fibres are ‘opened’ and blended after which they are conveyed to the card by air transport. They are then combed into a web by a carding machine, which is a rotating drum or series of drums covered by card wire (thin strips with teeth). The precise configuration of cards will depend on the type of fibre and the basis weight to be produced. The web can be parallel-laid, where most of the fibres are laid in the machine direction, or they can be randomised. Typical parallel-laid carded webs result in good tensile strength, low elongation and low tear strength in the machine direction and the reverse in the cross direction. Machine parameters and fibre mix can be varied to produce a wide range of fabrics with different properties.
2.Web bonding
Webs have a limited initial strength right after the web formation (depending on various bonding mechanisms). The web needs therefore to be consolidated in one or the other way. The choice of the web consolidation method strongly depends on functional properties that are needed as well as on the type of fibres used..
There are three basic types of bonding:
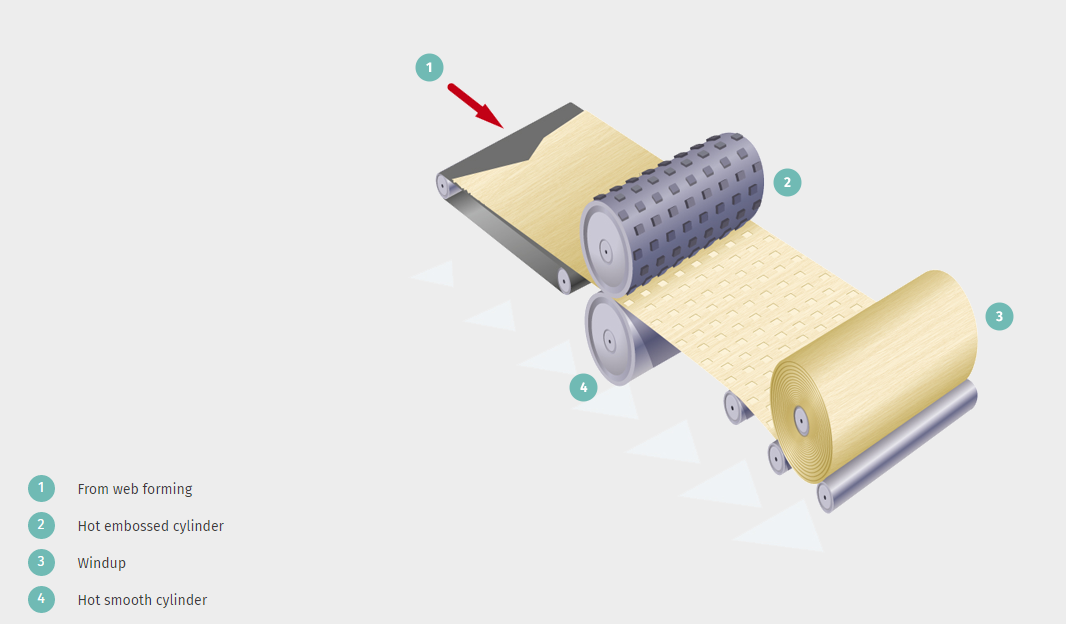
This method uses the thermoplastic properties of certain synthetic fibres to form bonds under controlled heating. In some cases, the web fibre itself can be used, but more often a low melt fibre or bicomponent fibre is introduced at the web formation stage to perform the binding function later in the process.
There are several thermal bonding systems in use:
Calendering uses heat and high pressure applied through rollers to weld the fibre webs together at high speed.
Through-air thermal bonding makes bulkier products by the overall bonding of a web containing low melting fibres. This takes place in a carefully controlled hot air stream.
Drum and blanket systems apply pressure and heat to make products of average bulk.
Ultrasonic bonding is a technology in which molecules of the fibres are being ‘excited’ under a patterned roller by high frequency movement of a ‘sonotrode’ which produces internal heating and softening of the fibres.
3.Finishing treatment
The opportunity to combine different raw materials and different technologies accounts for the diversity of the industry and its products.
This diversity is further enhanced by a range of finishing treatments. By finishing the nonwoven can be tailored or functionalized to meet specific properties. Finishing treatments can be either mechanical (stretching, perforating, crimping etc) or chemical. With the latter one can modify the surface of the fibres and the nonwoven to change the haptics or the repellency of the nonwoven.
Nonwovens can be made conductive, flame retardant, water repellent, porous, antistatic, breathable, absorbent and much more. They can also be coated, printed, flocked, dyed or laminated to other materials.
Converting
Nonwoven manufacturing ends usually with large rolls of product. Converters convert -as the word says- this roll good into a consumer product.
Sometimes converting is done in 2 steps. Before manufacturing the finished product one might want to bring the rolled good one step closer to the final product by slitting, cutting, folding, sewing or heat sealing.

Promoting sustainability of nonwoven
We understand sustainability as affirmative action to minimise negative impact on the environment and to create positive environmental, social and/or economic developments in the activities of the nonwovens industry. This is to be created in close dialogue and partnership with all of our stakeholders.

The Suntech Sustainability Vision
Suntech developed a Sustainability Vision 2030, giving clear insight into the priority topics on sustainability for our industry.
The vision combines the most prominent topics of the materiality matrix with key United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDG's) for the industry. The four key areas are: Sustainable supply chain, Eco-efficient, Building trust and Responsible end of life. Each area is defined by a clear ambition.
The vision aligns the industries’priorities and allows the industry to collectively head in the same direction. It should be interpreted as a guideline rather than a rule to help our members identify their priorities and further develop their own sustainability strategy. suntech’s role is to facilitate interaction and help the industry progress towards their sustainability goals in line with the United Nation's SDG’s.

(Suntech ST-SMS composite nonwoven production line)
Product stewardship
suntech’s mission for the last 50 years has been to support the industry, especially in areas of performance and safety requirements
Product stewardship encompasses the environmental, health and safety dimensions of a product and everyone, involved in its life cycle. The nonwovens industries’ approach for a sound product stewardship materialises through different approaches such as the development of technical standards, the investment in better and innovative technologies, the adoption of regulations where necessary, the continuous efforts towards more sustainability and the dialogue with consumers and stakeholders.
suntech supports its members’efforts activities in the dialogue with stakeholders, in the development of position papers, test method and regulatory solutions. This approach towards product stewardship is a strong part of the global message our team is spreading in conferences and symposiums across the world.

(Suntech ST-AMB Meltblown machine)
Quality and Audit programme (QAP)
Within the supply chain of absorbent hygiene products many quality audits are being conducted on an ongoing basis. As there are multiple quality standards out there and multiple companies may unintentionally duplicate the audit of a single supplier. This audit system can be improved by creating a harmonised standard and removing redundant audits. Two years ago the was exactly the idea that led towards quality assurance programme.
QAP is a Quality, auditing and certification programme
It is a quality programme, based on a harmonised quality standard.
After a number of preliminary meetings and workshops in which the idea has been discussed the standard has been drafted by an expert panel of members, using the best available standards as a basis. This work has been completed in the summer of 2019, resulting in a preliminary but agreed standard.
To be effective it needs to be implemented by companies in the supply chain and will be audited in an objective and consistent way. A series of 20 pilot audits will be carried out over 2020 by BSI, the British Standardisation Institute who suntech members have assigned with this task after a careful supplier evaluation and selection procedure.
With 50 years of technical precipitation and design experience, suntech has developed and produced intelligent non-woven fabric machines, including spunbonded non-woven fabric machines, spunmelt non-woven fabric machines, melt blown machines, etc., to help human health and care for everyone's lives.
(Suntech ST-ASS spunbond nonwoven machine)

